

產(chǎn)品中心


AMPA Receptor 4(GluA4) Rabbit pAb
 一鍵復(fù)制產(chǎn)品信息
一鍵復(fù)制產(chǎn)品信息| 50μL | ¥1280.00 |
| 100μL | ¥1980.00 |
關(guān)閉
在線咨詢
Online consultation
-
在線咨詢
-
技術(shù)支持

關(guān)注微信公眾號(hào)

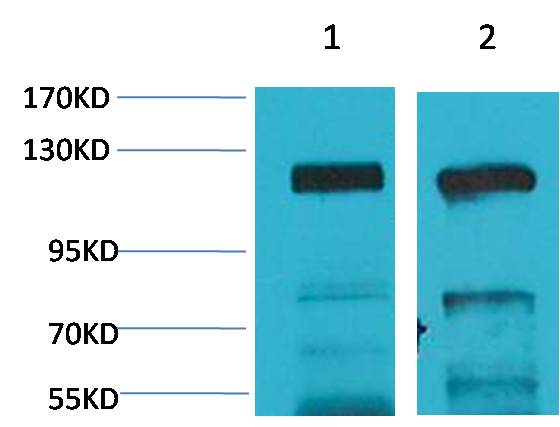
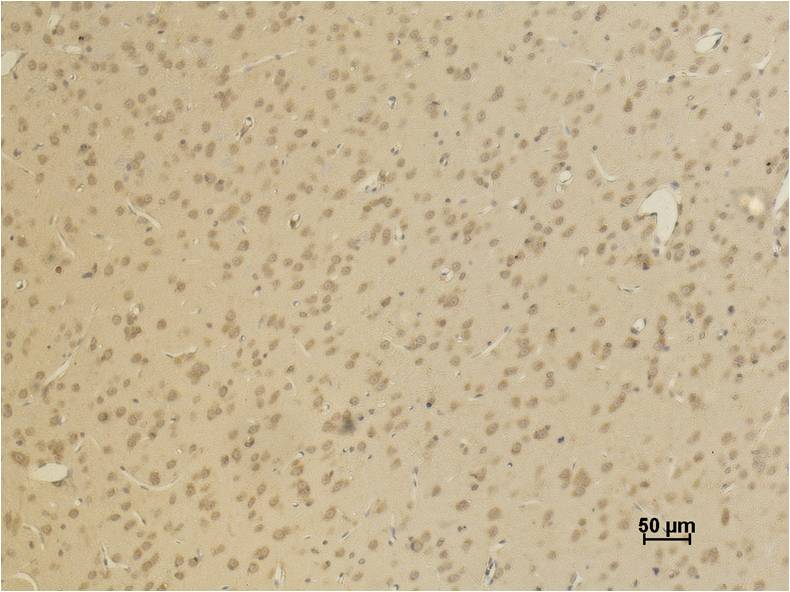
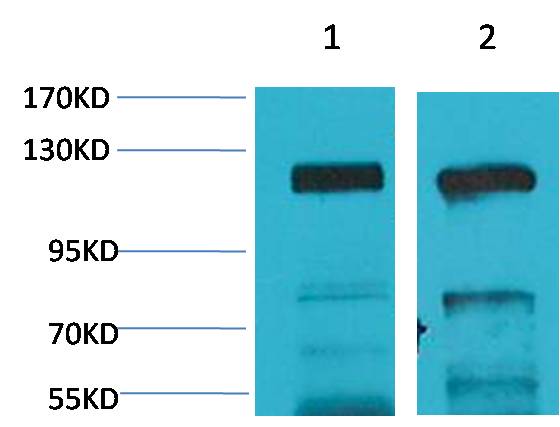
 下載說(shuō)明 ①
下載說(shuō)明 ①



